Precision is the foundation of great architecture. With 3D laser scanning, accuracy reaches an entirely new level.
Architectural surveys are evolving at an unprecedented pace, thanks to 3D laser scanning, a technology that combines speed, precision, and digital integration. By capturing millions of data points in mere moments, it provides architects and engineers with highly detailed and accurate representations of physical spaces. This article explores how this cutting-edge tool is transforming the field and why it’s becoming indispensable for professionals.
I. What is a 3D Laser Scanning ?
A 3D laser scanner is a device that uses lasers to measure and capture spatial data. It generates a “point cloud,” a dense collection of millions of points that precisely map the dimensions and geometry of a physical space or object.
Imagine capturing an entire building's geometry down to the millimeter in just a few hours.
How it works:
- Laser Emission: A laser beam scans the environment.
- Data Capture: The scanner measures the time taken for the laser to return after hitting a surface (Time of Flight method).
- Point Cloud Generation: The collected data forms a digital representation of the space.
II. Comparison: Traditional Surveys vs. 3D Laser
3D laser scanning reduces human error, saves time, and provides vastly superior data quality.
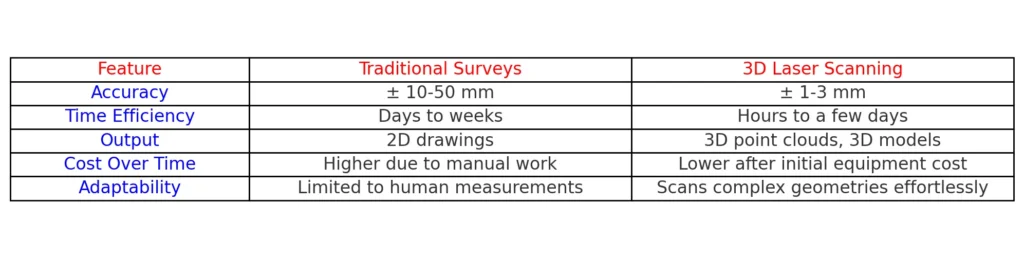
The difference between manual measurements and 3D laser scanning is like comparing a typewriter to a modern laptop.
III. The Advantages of 3D Laser Scanning for Architectural Surveys
- Unmatched Precision: Captures even the smallest architectural details, ensuring complete accuracy.
- Speed: Surveys that once took weeks can now be completed in days or even hours.
- Digital Integration: Data integrates seamlessly into BIM software for design, planning, and maintenance.
- Preservation of Historical Sites: Scanning enables virtual preservation and accurate restorations.
- Reduced Human Error: Eliminates inaccuracies from manual measurements.
Example: The Notre Dame restoration project heavily relied on 3D laser scanning to recreate its precise dimensions post-fire.
Efficiency meets precision: the hallmark of 3D laser scanning.
IV. Integration of 3D Data in BIM Software
The integration of 3D laser scanning data into BIM (Building Information Modeling) platforms has revolutionized how architects and engineers approach projects. By converting the raw point cloud data into actionable 3D models, professionals can streamline workflows, reduce errors, and improve collaboration. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
Point Cloud Capture:
- After completing a 3D laser scan, the scanner generates a “point cloud,” a digital representation of the surveyed space.
- This raw data is often large and unstructured, requiring specialized software for refinement.
Data Import into BIM Software:
- Leading BIM tools like Revit, ArchiCAD, and Navisworks support point cloud imports.
- Tools such as Autodesk ReCap or CloudCompare preprocess the data for compatibility.
Modeling and Reconstruction:
- The imported point cloud serves as a reference for creating accurate as-built 3D models.
- Users can overlay designs onto the scanned environment, allowing for clash detection, spatial planning, and renovation analysis.
Analysis and Simulation:
- BIM platforms enable analysis of scanned data for energy modeling, structural assessments, or performance simulations.
- This is particularly valuable for projects requiring retrofits or sustainability upgrades.
Collaboration and Sharing:
- BIM platforms support file-sharing formats like IFC or BCF, enabling smooth communication among stakeholders.
From scan to model, BIM software bridges the gap between reality and design.
V. Equipment and Reference Brands for 3D Laser
Investing in a reliable 3D laser scanner ensures accurate data capture and a smoother workflow. Various brands cater to different needs, from compact, portable devices to high-end, industrial-grade scanners.
Top brands in 3D laser scanning include:
- Leica Geosystems: Renowned for high-precision scanners like the BLK360.
- FARO Technologies: Offers portable scanners for indoor and outdoor use.
- Trimble: Known for robust and versatile devices like the TX series.
- Matterport: Popular for 3D virtual tours and real estate applications.
- Topcon: Reliable for large-scale infrastructure projects.
From scan to model, BIM software bridges the gap between reality and design.
VI. Alternatives to 3D Scanner: LIDAR iPhone Applications and Other Tools
- Overview: Polycam is one of the most popular LIDAR apps for creating high-quality 3D models directly from your smartphone or tablet.
- Use Case: Perfect for interior design, quick architectural surveys, and creating digital twins of physical spaces.
Moasure
- Overview: Moasure isn’t a LIDAR app but a smart measuring tool that combines motion sensors and advanced algorithms to calculate distances, angles, and areas.
- Use Case: Great for site measurements, landscaping, or room planning without needing a full 3D model.
Canvas
- Overview: Canvas is a LIDAR-based app designed specifically for professionals in construction, design, and remodeling.
- Use Case: Best for remodeling projects, renovations, and interior design workflows that require quick and accurate space documentation.
With tools like Polycam, Moasure, and Canvas, precision surveying is now more accessible than ever, empowering professionals to achieve exceptional results without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
With its unparalleled accuracy, speed, and digital capabilities, 3D laser scanning is transforming architectural surveys. From precise restoration projects to seamless BIM integration, this technology empowers architects and engineers to innovate and deliver exceptional results. Whether you’re working on large-scale developments or preserving cultural heritage, 3D laser scanning is your ultimate ally in shaping the built environment of tomorrow.
Find the best Architectural scanning tool!
The future isn't measured by tape; it's scanned in 3D.